The most significant difference between NFVO and VNFM is VNFO is responsible for Network Service (NS) meanwhile VNFM is responsible for VNF. NS is a collection of multiple VNFs, each VNF can be deployed as multiple virtual server on top of VIM.
The below picture is the high-level architect of NFVO. It contains fundamental and mandatory elements based on the proposal of ETSI. We will go along with each of them and discuss about the general usage of each element.
In this picture, we can see that all the service is connected through API (mostly REST API). Some of them need communication channel AMQP such as OpenStack services. Others can be implemented as individual services.
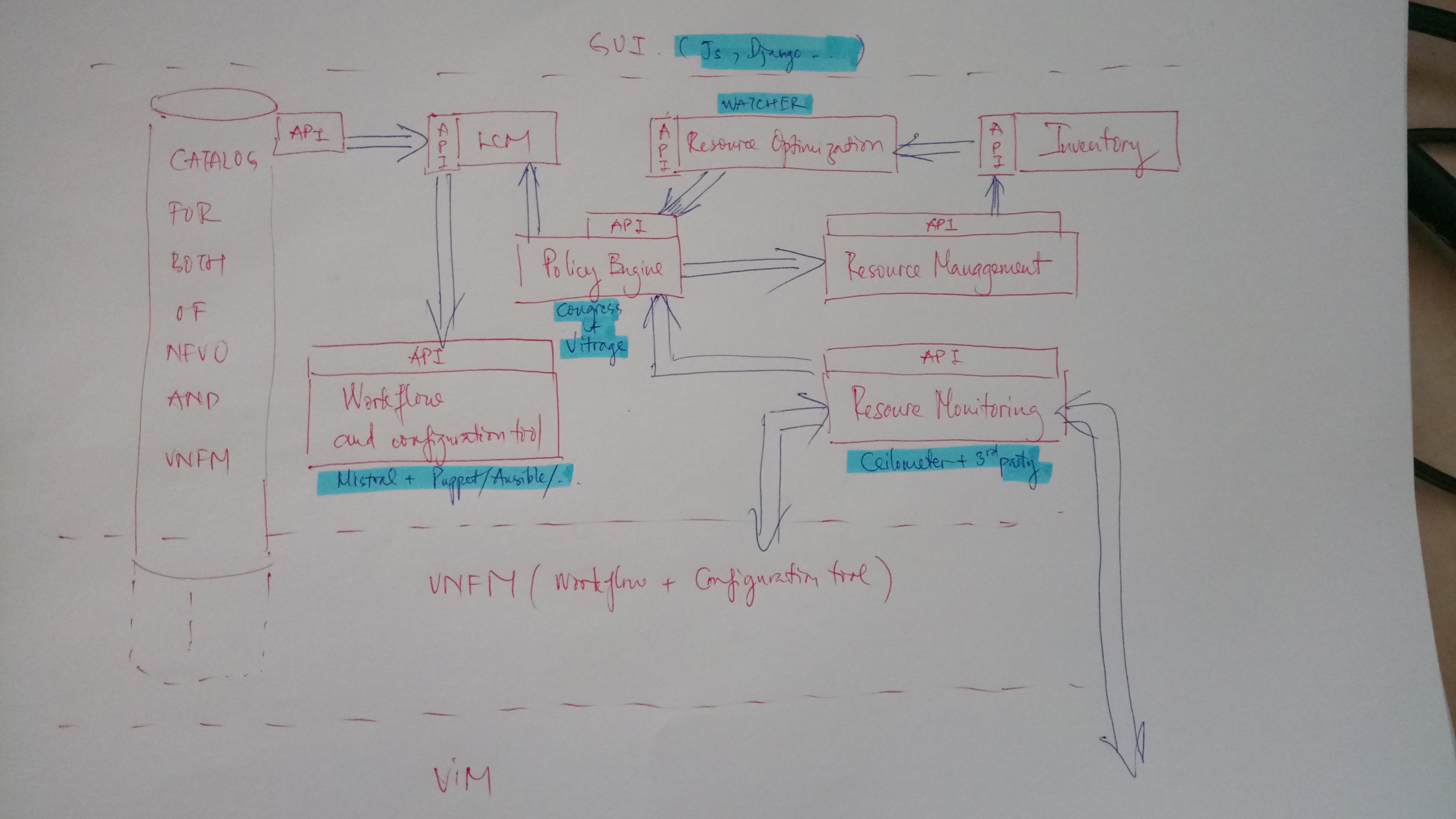
LCM: Life Cycle Management:
It manages the life cycle of NS that are NS INITIATE, NS TERMINATE, NS SCALE, etc. It will interact with catalog where NS Description (NSD) is stored to get the description. Then it will talk to workflow and configuration service to execute actions of NS. Since NSD contains information of both of underlaying element such as network, SDN resources, etc. and VNF Description (VNFD) so that the workflow in NFVO will interact with VNFM to deloy VNF, configuration tool in NFVO will configure the underlaying elements by talk to VIM.
Besides, it also gets information from policy engine about NS usage policy as well as the monitoring/alarms of root analysis. Based on this information, LCM will trigger the appropriate actions such as TERMINATE, SCALE, etc.
Resource Management:
It defines the templates of resources such as VIM, SDN, tenants, etc. When the client uses the GUI to fill out the information of NS, they should also provide the information of underlaying resources such as type of VIM, name of tenants, network information of VIM, etc. These information will be filled out into templates that resource manager manage. After filling, resource manager will store these templates to inventory. Besides, these templates are also fetched to the NS related actions therefore monitoring services could override the information to the templates later.
Inventory:
Works as interface that get the templates from resource management and stores them into db. It also contains the dao interface to interact to db (mongodb, mysql, posgres, etc.).
Resource optimization:
It gets the templates of resources from Inventory that are filled up with the information of NS provided by client then by achieving the monitoring information through policy engine, it will decide the optimistic way to deploy NS, for instance, which compute host VNF should be deployed. Project Watcher of OpenStack implements the theory of action plan of learning machine is a potential candidate of this service.
Policy Engine:
It will provide the mechanism of policy based resource usage. For instance that you want to have compute 1 of VIM available for 30 days from now and then sleep. It may/may not include the engine of root analysis which is responsible for failures. Vitrage is a potential candidate here. We can separate vitrage to be an individual element.
Resource monitoring:
It is the monitoring solutions for resource usage of VIM. This service should talk to VNFM or directly VIM. It then sends information of monitoring to Policy Engine and this information will be fetched to resource management and resource optimization process.
Catalog:
This is a service which store information of NS. This information can be a zip/tar file that contains the templates of NS. The most popular of template format is TOSCA.
Summary:
NFVO is just only a software that should run in a server (physical or virtual). However, it should be packaged into an image file that contains all its dependencies, libraries in order to decrease the NFVO deployment time.
20/1/2017
VietStack team

Comments